Table of Contents
Why Device Management is Crucial for Google Workspace Admins
Keeping in mind how often companies have data leaks and breaches due to extremely mundane factors (for example, an employee accessing a sensitive company’s data using someone else’s device and public WiFi connection), the security and efficiency of device management cannot be overstated.
For Google Workspace admins, especially in companies that try to adhere to compliance standards and protect their data, ensuring that all devices conform to organizational policies and security standards is vital. This is not just about securing data; it’s also about enabling smooth and secure operations across an increasingly remote, global or hybrid workforce, as we see that many employees now work from home or from remote locations. Effective device management aims at preventing unauthorized access, protects sensitive information, and helps maintain operational continuity.
What Does Device Management Entail
Device management includes several critical activities:
● Device Tracking and Inventory Management
Keeping an up-to-date record of all devices accessing corporate data.
● Security Policy Enforcement
Applying security policies across devices, such as password protection and encryption.
● Remote Management
Performing remote actions like device locking or data wiping in case of theft or loss.
● Compliance Monitoring and Reporting
Regularly auditing device usage to ensure compliance with corporate and regulatory standards.
Device Management Options: Manual vs. Automated Tools
Google admins, just like all other IT professionals, can approach the task of device management in various ways.
Manual Management: Unfortunately, the most common one. Involves physical checks and individual device handling. Why it is not the best option? This approach is very time-consuming and prone to errors. Besides, if your headcount exceeds 50 employees tracking everyone’s device is pretty much physically impossible even for the most dedicated Google admin.
Google Admin Console: This powerful and most commonly used tool definitely provides ways for bulk device management actions, security policy enforcement, and basic compliance monitoring. Admin Console is very effective for routine tasks, and the only challenges it might have arise when it comes down to integrating these actions into broader operational workflows.
GAM (Google Apps Manager): a popular command-line tool developed specifically for Google Workspace administrators to manage domain and user settings in bulk. It definitely allows to do much more than just through using Admin Console alone. Using GAM, administrators can fetch reports on device status, enforce policies, and perform actions like account wipes or password resets on devices. GAM also helps enforce security policies consistently. Commands can be scripted to regularly check and enforce compliance across all devices, ensuring that any deviations are quickly addressed.
Third-Party Google Admin Tasks Automation Tools: Google Admin tasks automation solutions like Zenphi offer capabilities that one might call “Google Console on steroids”. They allow you to perform all the familiar actions that you would need to perform using Google Admin Console but faster, and embed them into larger, automated workflows.
Zenphi vs. Google Admin Console Vs. GAM: A Workflow Perspective
While both the Google Admin Console and GAM are effective for direct and bulk but stand-alone device management tasks, Zenphi takes it a step further by integrating these tasks into comprehensive workflows. These are the core differences:
Comprehensive Process Integration
GAM is very efficient for large-scale changes and can execute complex queries and bulk operations quickly. However, it does not inherently support linking these commands into multi-step workflows. For example, after initiating a command like device provisioning, as an admin, you’d need to manually monitor the process and input further commands to initiate subsequent steps, such as setting device configurations or assigning devices to users.
The Admin Console is user-friendly and designed for direct interaction with less technical users. It allows for basic automation and management tasks, however, just like GAM, you can’t build multi-step workflows using Admin Console. It’s great for manual intervention and management of small teams and processes but when the business scales, Console capabilities create huge limitations.
With Zenphi, admins can create workflows that go beyond listing devices or enforcing policies. A single workflow could automate the entire process from device listing to audit trials and communication with the management.
Custom Alerts and Notifications
With Google Admin Console administrators can set up alerts for specific events like login attempts, settings changes, or security incidents within the Google Workspace environment. However, notifications are typically standard and may not cover all scenarios or be easily tailored to specific organizational needs.
GAM itself does not have built-in capabilities for sending alerts or notifications. You can’t use GAM to monitor events and trigger responses. To achieve the result you’re looking for, you’ll have to script custom monitoring solutions or integrate GAM with other tools. For instance, a script could run periodically to check for specific conditions and use an external service (like sending an email via SMTP or integrating with a messaging service) to send alerts.
Unlike both of those tools, Zenphi allows for fully customizes alert configuration. In our practice, when a device is red-flagged, Google admins use Zenphi to receive notification but also automatically find and notify relevant managers, alert the IT team, and assign tasks to initiate preventive measures — all without manual intervention other than building the workflow itself. Zenphi also helps to schedule ongoing unauthorised access audits, taking security to a completely different level, absolutely hustle-free.
Best Practices For Google Admin: Automated Device Audit In Google Workspace
This part of the blog post is a description of the workflow that is used actively by one of our customers to improve their device audit process, enhance their compliance level and ensure 100% security of data in Google Workspace, despite the fact that about 45% of their employees work remotely or use a hybrid setup. Let’s dive in.
- Company size: 10000 employees
- Working environment: remote + hybrid
- Compliance standards: HIPPA, GDPR, ISO 27001
This is how their workflow looks like.
Step 1: Creating a Main Folder for the Current Devices Audit
The first part of the flow built upon the best practices involves creating a dedicated folder to store all audit files from the every run. In Zenphi, use the “Create Folder” action, which allows to set up a new Google Drive folder.
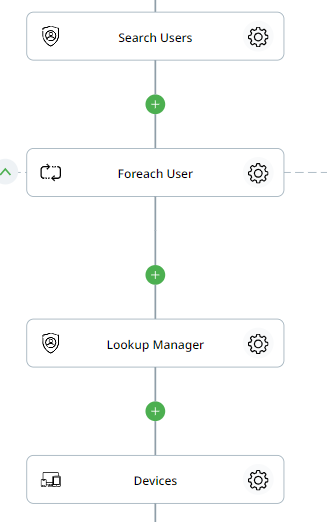
Step 2: Retrieving User and Device Information
The next portion of the flow focuses on searching for users in the Workspace and retrieving their device information (performed by using a “Search Users” action in Zenphi).
Step 3: Finding a Manager
As we said, notifying a relevant manager about devices that new devices were added to the list. This step is also used quite often in building approval flows — when Google admin assign a task to a relevant manager to approve a new device. In this case, it will be added to the directory of the approved devices automatically. This step is performed by using a “Lookup Manager” action (manager’s contact details are retrieved from a previous step).
Step 3: Finding a Manager
As we said, notifying a relevant manager about devices that new devices were added to the list. This step is also used quite often in building approval flows — when Google admin assign a task to a relevant manager to approve a new device. In this case, it will be added to the directory of the approved devices automatically. This step is performed by using a “Lookup Manager” action (manager’s contact details are retrieved from a previous step).
Step 4: List devices
The device auditing process obviously involve listing devices info which returns all devices, their last sync, status, and much more. Also can be perform easily using Zenphi just by adding “List Device Info” action to the workflow.
Step 5: Creating an Audit Report
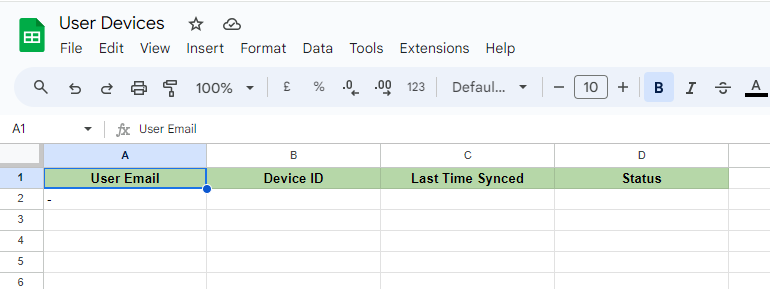
The best practice and the necessary part of every audit is the report. In Zenphi, you can configure your workflow in a way that your device deport will be generated and emailed to relevant stakeholders automatically.
For this, Google admin has to create a Google Sheets template that will be reused each time a report needs to be generated. This is how it might look like.
When the flow is active and recurring audits are run automatically, and there is a case of 1 or more devices found, Zenphi creates a new Google sheet file using the above mentioned template (in the flow it is performed via the “Copy File” action and “Add Multiple Rows” action that adds all detected devices at once).
The best way to handle the report further is to export the Sheets to PDF format (in Zenphi builder it’s performed via “Export to PDF” action).
Step 6: Notifying the Manager
Next step of the workflow is to email this PDF to a relevant manager identified in the beginning of the process (in Zenphi, use “Send an Email (Gmail)” action).
Step 7: Kickstarting the process
To trigger this process we recommend using a Start on a Custom date and time option and just let it run every 5-10 days starting from today. This way, you will ensure that device audits are performed in your company consistently and using all the best practices.